‘Xylitol helps prevent as well as reverse tooth decay’
Xylitol dental benefits on oral health has been recognized by The American Academy of Paediatric Dentists (AAPD) to include a significant reduction in tooth decay, as well as contributing to the reversal of cavity formation.
Dental cavities occur when natural bacteria present in the mouth feed on the sugars, we eat which remain on the teeth. These bacteria multiply and produce acids that attack the teeth and form cavities, or decay. The bacteria are unable to feed on xylitol and are essentially starved and cannot grow
Studies show that Xylitol dental benefits include effectively decrease acid-producing bacteria by up to 90%.
Xylitol use has been found to significantly reduce tooth decay in both high and low risk groups concerning cavity occurrence.
What causes Cavity & How xylitol controls cavity?
Cavity occurs when-
- Bacteria in your mouth feed on sugary, starchy foods and drinks (fruit, candy, bread, cereal, sodas, juice and milk). The bacteria convert these carbohydrates into acids.
- Ph of saliva decreases due to the acids. The minerals (Ca++ and PO4-) start moving out of teeth in acidic media causing demineralisation.
- Demineralisation damages tooth enamel causing pre-cavity lesions and cavity.
- Bacteria, acid, food and saliva mix to form dental plaque. This sticky substance coats your teeth.
- Without proper brushing and flossing, the plaque keeps on depositing over the tooth surface causing gum problems.
Double Action of Xylitol on Cavity
- Inhibition of new cavity formation
- Reversal of cavities and pre-cavity lesions
Inhibition of new cavity formation
Cavity forming process is inhibited by inhibition of demineralisation. Xylitol is believed to inhibit enamel demineralization in several ways:
- Xylitol is thought to associate with calcium, which can inhibit the dissolution of calcium and phosphate ions from enamel.
- Xylitol is thought to act as a carrier of calcium, which is needed for enamel remineralization.
- Xylitol can remineralize deeper layers of demineralized enamel by making it easier for calcium to move and be accessed.
- After being absorbed by bacterial cells, xylitol is converted into X5P, which can inhibit bacterial metabolism and acid production.
Process of cavity inhibition-
- Xylitol inhibits the growth of cavity causing bacteria; hence no more acid is produced.
- Xylitol neutralizes already present acid in the mouth and helps control demineralisation.
- Xylitol stimulates saliva production which prevent bacteria from adhering to the tooth surface thus inhibiting plaque formation.
- Xylitol increases salivary PH and hence the minerals (Ca++ and Po4- ions) start moving into the tooth. Hence, no further de-mineralisation and no cavity.
Reversal of cavity and pre-cavity lesion
Reversal of cavity happens due to repair of enamel by remineralisation. Xylitol promotes remineralisation in several ways:
- Increasing saliva production: Xylitol stimulates saliva production, which helps repair damaged enamel and remineralize teeth.
- Reducing plaque: Xylitol reduces plaque formation by preventing bacteria from adhering to teeth.
- Increasing pH level: Xylitol doesn’t break down like sugar does, which raises the pH level in saliva and prevents the formation of acid.
- Facilitating Ca2+ movement: Xylitol can induce remineralization of deeper layers of demineralized enamel by facilitating Ca2+ movement and accessibility.
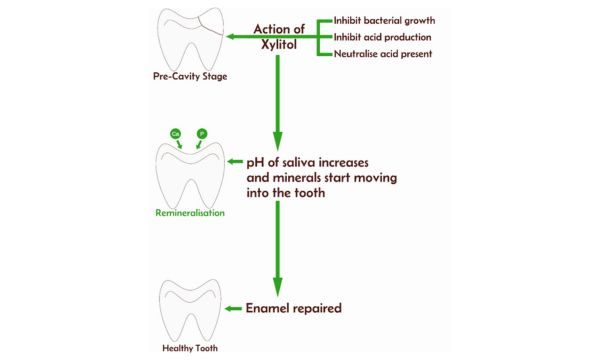
Process of cavity reversal
Reversal of cavity happens only when the cavity is limited to the outer most layer (the hardest layer enamel is the outer most layer) of tooth. Once it penetrates deep and contaminate other layers (dentin or pulp) of the tooth, cavity reversal is not possible. But with the use of xylitol, further damage to the tooth can be minimised.
- With remineralisation repairing of enamel starts.
- Discoloration of tooth disappears as the minerals re-enter the tooth.
- Tooth regains its natural structure and pre-cavity/ early cavity is reversed.
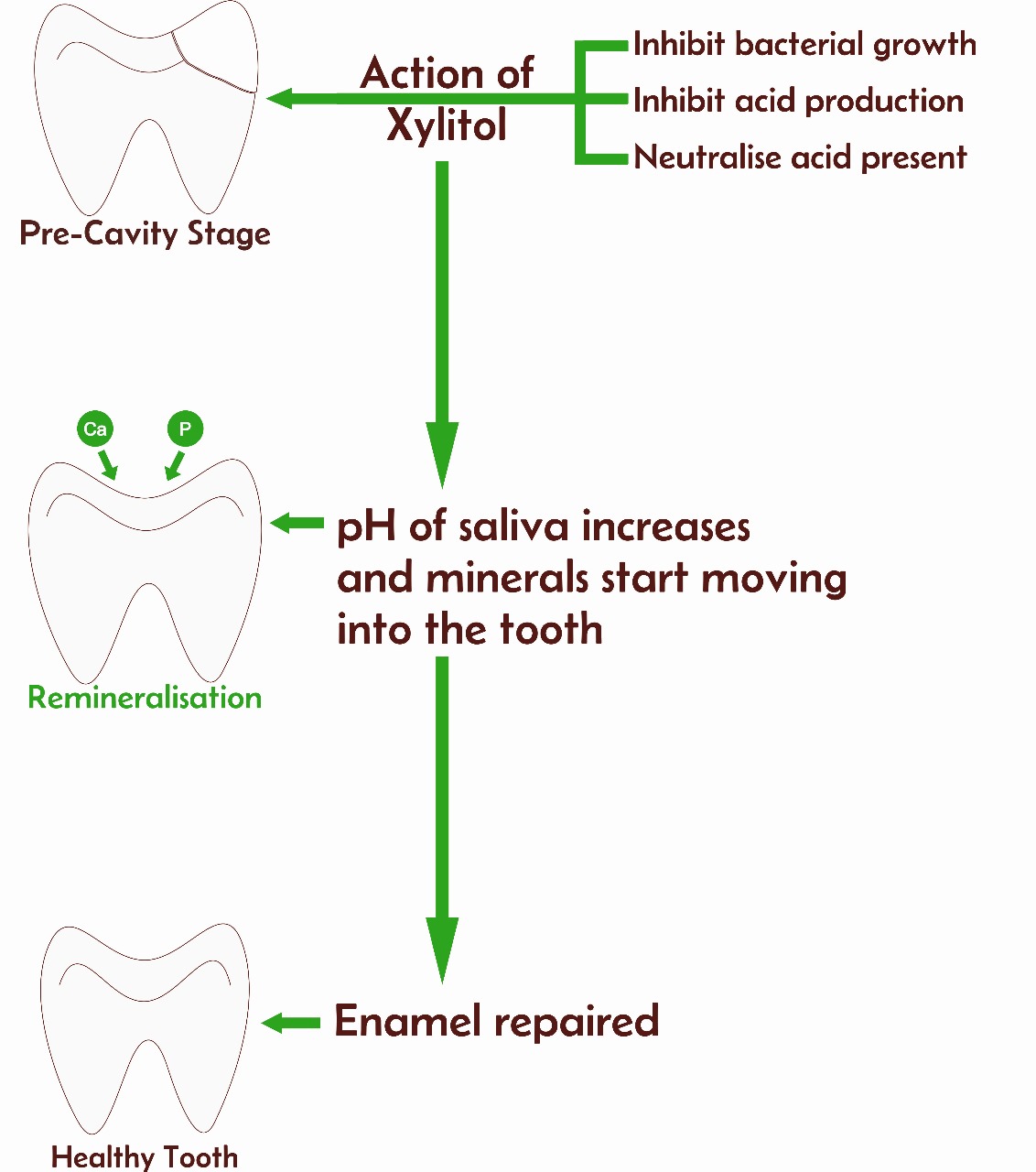
Process of cavity reversal
Reversal of cavity happens only when the cavity is limited to the outer most layer (the hardest layer enamel is the outer most layer) of tooth. Once it penetrates deep and contaminate other layers (dentin or pulp) of the tooth, cavity reversal is not possible. But with the use of xylitol, further damage to the tooth can be minimised.
- With remineralisation repairing of enamel starts.
- Discoloration of tooth disappears as the minerals re-enter the tooth.
- Tooth regains its natural structure and pre-cavity/ early cavity is reversed.
FAQs of Xylitol & Cavities
How does Xylitol acts on cavities (caries)
Contact Us
Customer support
+91-9310022929
care@bhoojaa.com
Our location
A-12 1st floor, Prashant Vihar, Rohini Delhi-110085