
What is Xylitol?
Xylitol is a naturally occurring sugar, antibacterial & anti-cavity in action, extracted mainly from ‘birch’ trees. It is also found in the skin of many fruits & mushrooms. Xylitol Has a Very Low Glycaemic Index and Doesn’t Spike Blood Sugar or Insulin. Though it looks and tastes like sugar, it has 40% less calories and hence safe for diabetic patients also. Xylitol contains zero fructose and has negligible effects on blood sugar and insulin.
Human studies demonstrate that xylitol — either by replacing sugar or adding it into your diet — can reduce cavities and tooth decay by 30–85%.
Xylitol can starve the harmful bacteria in your mouth, reducing plaque build-up and tooth decay. This can help prevent dental caries and inflammatory gum diseases.
What is Xylitol?
Xylitol is a naturally occurring sugar, antibacterial & anti-cavity in action, extracted mainly from ‘birch’ trees. It is also found in the skin of many fruits & mushrooms. Xylitol Has a Very Low Glycaemic Index and Doesn’t Spike Blood Sugar or Insulin. Though it looks and tastes like sugar, it has 40% less calories and hence safe for diabetic patients also. Xylitol contains zero fructose and has negligible effects on blood sugar and insulin.
Human studies demonstrate that xylitol — either by replacing sugar or adding it into your diet — can reduce cavities and tooth decay by 30–85%.
Xylitol can starve the harmful bacteria in your mouth, reducing plaque build-up and tooth decay. This can help prevent dental caries and inflammatory gum diseases.
Researches Prove “Xylitol the Star Performer”
Action of “Xylitol”
Anti- bacterial & Anti-cavity
Reduce plaque formation
Controls teeth sensitivity
Stimulates saliva production
Xylitol is an anti-inflammatory agent
Remarkable ulcer Healing Effect
Stops demineralization
Xylitol increases saliva rate and raises the pH of saliva
Stops the growth of cavity causing bacteria
Relieves dry mouth condition
Repairs damaged enamel
Increase salving PH
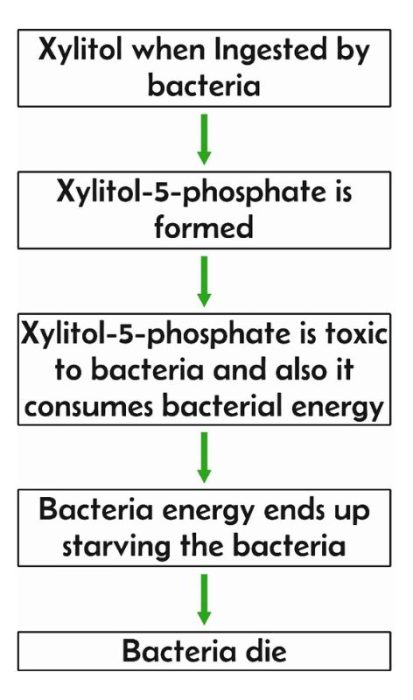
Xylitol may cause death of cavity causing bacteria when replaced with normal sugar in mouth
One of the leading risk factors for tooth decay is an oral bacteria called Streptococcus mutans. This is the bacteria most responsible for plaque.
Although some plaque on your teeth is normal, excess plaque encourages your immune system to attack the bacteria in it. This can lead to inflammatory gum diseases like gingivitis.
These oral bacteria feed on glucose from food, but they cannot use xylitol. As such, replacing sugar with xylitol reduces the available fuel for the harmful bacteria.
While these bacteria cannot use xylitol for fuel, they still ingest it. After absorbing xylitol, they are unable to take up glucose — meaning that their energy-producing pathway is clogged and they end up dying.
Other Potential Health Benefits of xylitol
Side effects of xylitol
Usage quantity of Xylitol
FAQs of xylitol
Contact Us
Customer support
+91-9310022929
care@bhoojaa.com
Our location
A-12 1st floor, Prashant Vihar, Rohini Delhi-110085

